Unveiling History of Science: The Origins of Knowledge
Explore the fascinating journey of how humanity has sought to understand the universe and our place within it. From ancient myths and early numerical systems to the birth of geometry and the dawn of scientific reasoning, discover the key milestones that have shaped our modern understanding of the cosmos and the world around us. This article delves into the historical roots of science and mathematics, highlighting the pivotal moments when human curiosity and intellect propelled us toward a more rational and evidence-based view of reality. Prepare to embark on a journey through time, tracing the evolution of knowledge and celebrating the power of human inquiry. This is the history of science.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Ancient Myths of Creation
- The Dawn of Numeracy
- Sumerian Contributions
- Egyptian Geometry
- Greek Rationalism
- Pythagoras: Numbers and Harmony
- Hippocrates and Natural Explanations
- Aristotle’s Influence
- Conclusion
Introduction to History of Science
For millennia, humanity has gazed at the stars, pondering the origins of the universe and our existence. Early cultures rooted their explanations in myth and legend, passed down through generations to explain the inexplicable. Today, armed with scientific tools and methodologies, we approach these questions with evidence-based inquiry. This article explores the transition from myth to science, highlighting key milestones in the development of human knowledge.
Ancient Myths of Creation
Diverse cultures around the world have creation myths that attempt to explain the beginning of everything. These narratives often involve gods or supernatural beings who shape the world from chaos or nothingness.
The Congo Creation Myth
Among the Bushoong tribes in Central Africa, the myth of Bumba tells of a creator god who vomited forth the sun, moon, stars, and eventually humans.
This myth illustrates the common theme of creation arising from a divine being or force.
Common Threads in Creation Myths
Many creation myths share common elements, such as the idea of a primordial void or chaos from which order is created. These stories reflect humanity’s innate desire to understand our origins and find meaning in the universe.
The Role of Myths
While not scientifically accurate, myths play a crucial role in shaping cultural identity and providing a framework for understanding the world. They offer explanations for natural phenomena and establish moral codes.
The Dawn of Numeracy in the History of Science
The ability to count and understand numbers is a fundamental aspect of human intelligence. The discovery of the Ishango Bone provides evidence of early numeracy skills dating back tens of thousands of years.
The Ishango Bone
Discovered in Central Africa in 1960, the Ishango Bone is a baboon fibula with a series of notches carved into it.


These markings suggest an understanding of counting, addition, and subtraction, indicating that humans were developing mathematical concepts as early as 37,000 years ago.
Significance of Numerical Understanding
The development of numeracy skills marked a significant step in human cognitive evolution. It allowed for more complex forms of communication, organization, and problem-solving.
Numbers as an Abstraction
The ability to abstract numerical concepts from concrete objects is a key distinction between human and animal intelligence. This abstraction paved the way for more advanced mathematical reasoning.
Sumerian Contributions to the History of Science
The Sumerians, who lived in Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq) around 6,000 years ago, developed one of the earliest writing systems and made significant advancements in mathematics.
The Birth of Writing
The Sumerians developed cuneiform, a writing system that used wedge-shaped symbols pressed into clay tablets.

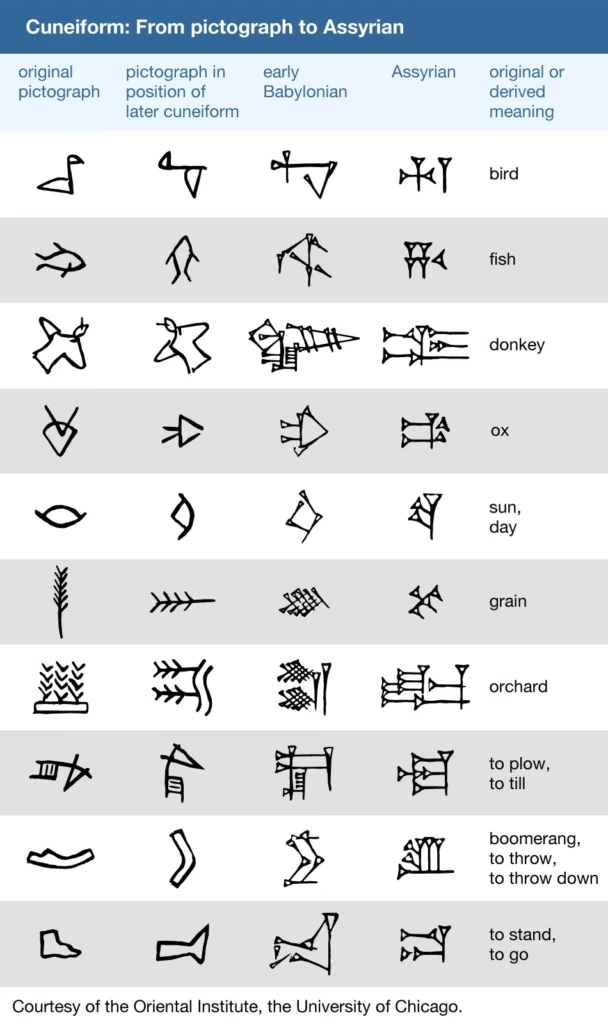
This allowed them to record information about agriculture, trade, and governance.
Number Systems and Symbols
Impact on Civilization
The Sumerian advancements in writing and mathematics laid the foundation for future civilizations to build upon. Their innovations facilitated trade, record-keeping, and the development of complex societies. Could the Sumerians have imagined that their base-60 system would still be telling us the time thousands of years later?
The Role of Egyptian Geometry in the History of Science
The ancient Egyptians developed practical geometry to solve real-world problems related to land surveying and construction, particularly along the Nile River.
The Nile and Land Division
The annual flooding of the Nile River would wash away land boundaries, requiring Egyptians to re-measure and redistribute land each year. This led to the development of geometric techniques for calculating area and volume.
Practical Applications
Egyptian geometry was primarily focused on practical applications, such as constructing pyramids, temples, and irrigation systems.

They developed formulas for calculating the area of rectangles, triangles, and circles, as well as the volume of pyramids and cylinders.
The Book of the Dead
The Egyptians took land ownership so seriously that their religious book, the Book of the Dead, contained warnings about the punishment for stealing land.
Role of Greek Rationalism in the History of Science
The ancient Greeks transformed geometry from a practical tool into a system of abstract reasoning and logical deduction. They sought to understand the underlying principles of mathematics and the natural world.
The Shift to Abstract Thought
Unlike the Egyptians, who focused on practical applications, the Greeks were interested in the theoretical foundations of mathematics. They developed the concept of proof, using logical arguments to establish the truth of mathematical statements.
The role of the Union of Science and Mathematics in the History of Science
The Greeks recognized the power of mathematics to explain the natural world. This marked the beginning of a long and fruitful relationship between science and mathematics.
Legacy of Greek Mathematics
Greek mathematicians such as Euclid, Archimedes, and Pythagoras made groundbreaking contributions to geometry, number theory, and calculus. Their work continues to influence mathematics and science today.
Pythagoras: Numbers and Harmony
Pythagoras, born in ancient Greece around 570 BCE, is often considered the first true mathematician. He believed that numbers held the key to understanding the universe and that everything could be expressed in terms of numerical ratios.
The Pythagorean Theorem
Pythagoras is best known for the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (a² + b² = c²).
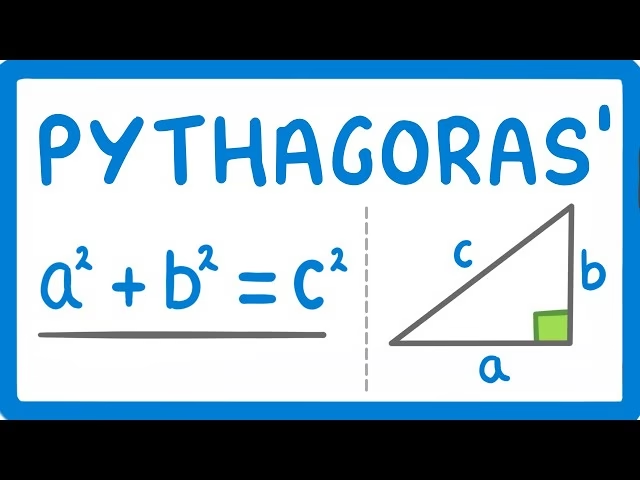
This theorem has countless applications in geometry, trigonometry, and engineering.
Music and Mathematics
Pythagoras also explored the relationship between music and mathematics. He discovered that musical intervals could be expressed as numerical ratios, leading him to believe that the universe was governed by mathematical harmony.
The Cosmos as Order
Pythagoras saw the cosmos as an ordered and harmonious system, with each part contributing to the whole. He believed that numbers could reveal the underlying structure of reality.
Hippocrates and Natural Explanations
Hippocrates, a Greek physician who lived in the 5th century BCE, is considered the father of medicine. He rejected supernatural explanations for disease and emphasized the importance of observation, diagnosis, and natural remedies.
Rejection of Divine Intervention
Unlike his contemporaries, who believed that illness was caused by divine punishment, Hippocrates argued that diseases had natural causes and could be understood through careful observation and reasoning.
The Hippocratic Corpus
The Hippocratic Corpus is a collection of medical texts attributed to Hippocrates and his followers.

These texts describe various diseases, their symptoms, and their treatments, with little or no mention of divine intervention.
Emphasis on Observation
Hippocrates emphasized the importance of observing patients and recording their symptoms. He believed that by carefully studying the course of a disease, physicians could develop effective treatments.
Aristotle’s Influence
Aristotle, a Greek philosopher who lived in the 4th century BCE, made significant contributions to logic, metaphysics, ethics, politics, and natural science. He developed a comprehensive system of thought that influenced Western intellectual history for centuries.
Logic and Reasoning
Aristotle is considered the founder of formal logic. He developed a system of syllogisms, which are logical arguments that consist of a major premise, a minor premise, and a conclusion. This system of logic became a cornerstone of scientific reasoning.
Classification of Animals
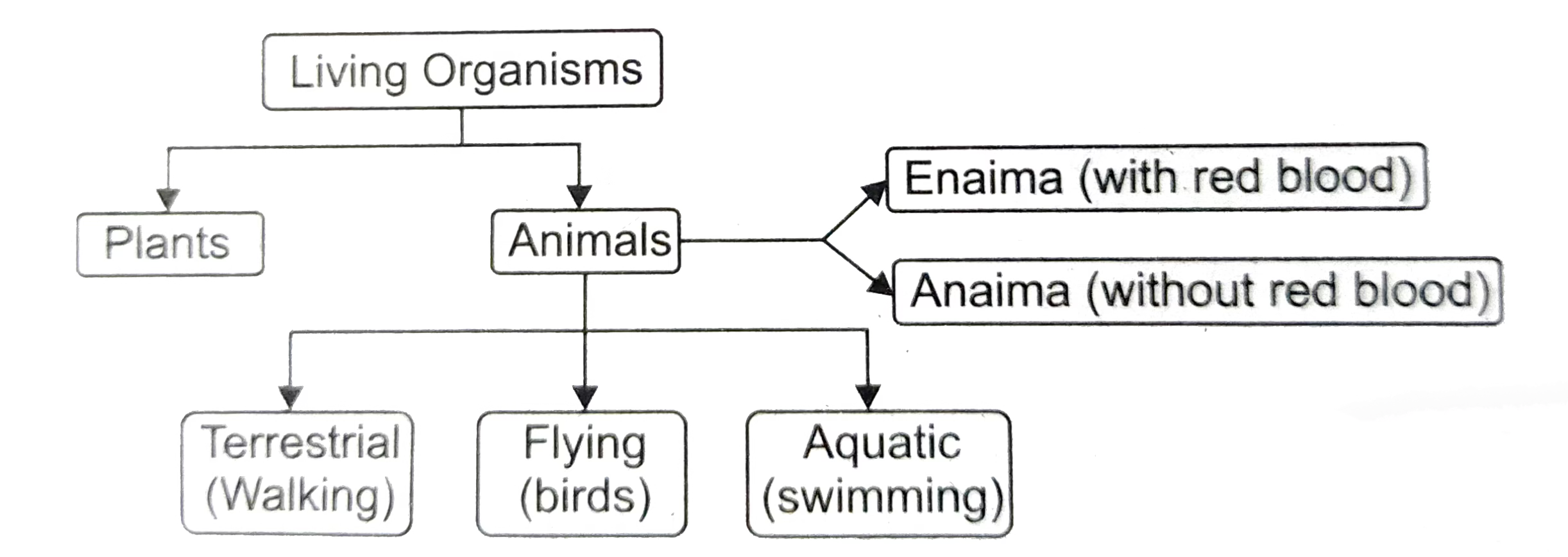
He divided animals into those with blood and those without blood, laying the groundwork for the science of zoology.
Earth as the Center
Aristotle believed that the Earth was the center of the universe and that the sun, moon, and stars revolved around it. While this view was later proven incorrect, it was the dominant cosmological model for centuries.
Conclusion
The journey from ancient myths to modern science is a testament to human curiosity and the power of reason. From the earliest attempts to explain the universe through stories to the development of mathematics, logic, and empirical observation, humanity has made remarkable progress in understanding the world around us. As we continue to explore the mysteries of the cosmos, let us remember the foundations laid by our ancestors and strive to build upon their legacy of knowledge and discovery. The journey of knowledge is like climbing a mountain; each step builds upon the last, offering a new perspective.
What aspects of the history of science and mathematics do you find most fascinating? Share your thoughts and continue exploring the wonders of the universe!
Like our content? Share and comment if you have any questions. You can also read about the AI protein folding problem that made Nobel Prize Winners.
This is just part 1; stay tuned for more parts. Meanwhile, watch the full video here!!

